Qventis shares the results of a recent study evaluating the safety and efficacy of RENÉE hyaluronic acid gels for tissue augmentation and facial wrinkles
At Qventis, we take inspiration from biological systems and make use of science to design products that exhibit features found in biological tissues. This is Bionic (from bion-, unit of life and -ic, like) design or biologically inspired engineering — the transfer of information from biological systems into the design of medical solutions. It is easy to understand that bionic designed products exhibit superior physical, chemical and biological compatibility and therefore are less prone to trigger side-effects; in other words, they have a high safety profile.

RENÉE, a set of bionic gels, is a versatile line with concentrations ranging from 18 mg HA to 28 mg of HA. The RENÉE product line is composed of a set of 4 dermal fillers — RENÉE SMILE (22 mg HA), RENÉE TOUCH (24 mg HA), RENÉE LIFT (26 mg HA) and RENÉE VOLUME (28 mg HA) and the skin booster RENÉE PRIME (18 mg HA). All products, including RENÉE PRIME, are formulated with crosslinked HA, with a crosslinking degree of 6% and are enriched with amino acids — glycine and proline. All RENÉE formulations are homogeneous, cohesive and true monophasic, thanks to an advanced manufacturing process, during which the HA chains are exposed to minimal mechanical and thermal stress.
Rheology profile
The rheology of a HA filler is crucial to understand its properties and to get the best aesthetic outcome for the patients. RENÉE family of dermal fillers has been designed to combine easy injection with good tissue integration while offering optimal lifting and volumizing effect rounded by natural, long-lasting results.
Regarding the basic rheological properties (G’, G” and tan δ) for RENÉE fillers; G’ and G” increase with the concentration of HA, as expected, so that a hydrogel with a higher concentration of hyaluronic acid also has the most pronounced volumizing effect.
Tan δ is an important parameter, which gives information about the hydrogel behaviour: when tan δ < 1, it means that we are dealing with a crosslinked hydrogel having an elastic modulus (G’) higher than the viscous modulus (G”), if tan δ > 1 the gel behaves as a viscous fluid. This is the case of RENÉE PRIME, our skin booster.
For the RENÉE set of fillers with concentrations ranging from 22 mg HA to 28 mg HA, rheological results show that tan δ is approximately constant, with a value between 0.4 and 0.5. This shows that the formulations of RENÉE fillers are hydrogels, having a good degree of viscosity. This is why RENÉE fillers are soft, well-hydrated, easy to inject and have excellent tissue integration.
The value of G’ for RENÉE fillers is carefully controlled so that it is never higher than 200 mPa in order to have the best combination of cohesivity, elongation and resistance for the hydrogel formulations. Thanks to an advanced manufacturing process, the RENÉE formulation hydrogels have a truly monophasic structure that, together with carefully tuned rheological properties, leads to a unique combination of cohesivity, elongation and resistance, which can be shown with a simple finger test.
In conclusion, RENÉE formulations have an unparalleled rheological profile with a unique combination of elasticity, cohesivity, and stretchability.
Evaluation of safety and efficacy of RENÉE BIONIC GELS
Study design
The aim of this open-label, retrospective, monocentric study was to evaluate the safety and efficacy of RENÉE hyaluronic acid gels for soft tissue augmentation and correction of facial wrinkles. The study was conducted between January 2021 and December 2021 at the Centro Medico Polispecialistico (CMP) in Pavia, Italy, by an unblinded treating investigator (TI) along with a blinded evaluating investigator (EI) who performed all safety and effectiveness assessments. Different areas of the face were treated. The investigator selected the product to use on the basis of the characteristics of the area to treat and determined the technique and injection volume based on clinical experience. No touch-up treatment was performed. All patients were followed up for 6 months. The TI took pictures of the patients at baseline, 1 week, 2 weeks, 4 weeks, and 24 weeks after the treatment. The pictures were taken with a classic 2D camera (Nikon D90) and with a 3D camera (LifeViz Mini) to evaluate efficacy and facial volume changes. All patients were asked to record post-treatment adverse and rate satisfaction with treatment.
Subjects
All patients were adults (aged ≥18 years) and provided informed consent. Subjects were excluded if they had undergone facial tissue augmentation in the lower two-thirds of the face with dermal fillers within the previous 12 months or with fat or botulinum toxin injections within the previous 6 months, or had received semipermanent fillers or permanent facial implants in the lower face. Subjects with uncontrolled disease, active inflammation, infection, lesions in the treated area, or who had a tendency for developing hypertrophic scarring were also excluded. Females who were pregnant or nursing were ineligible to participate. Drugs known to increase coagulation time were withdrawn for 10 days prior to and 3 days after study treatment.
Assessments
Clinical efficacy was assessed at 1 week, 2 weeks, 4 weeks, and 24 weeks post-injection by a blinded evaluating investigator (EI) comparing the pre-treatment pictures with the post-treatment pictures, using the Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale (GAIS). The GAIS rating categories represents a five-point scale, where 1 = very much improved; 2 = much improved; 3 = improved; 4 = no change; 5 = worse. All patients completed a 30-day safety diary after treatment reporting any injection site responses. In addition, subjects rated satisfaction with treatment 24 weeks post-injection using a 5-point Likert scale (1 = very satisfied, 2 = satisfied, 3 = indifferent, 4 = dissatisfied, 5 = very dissatisfied).
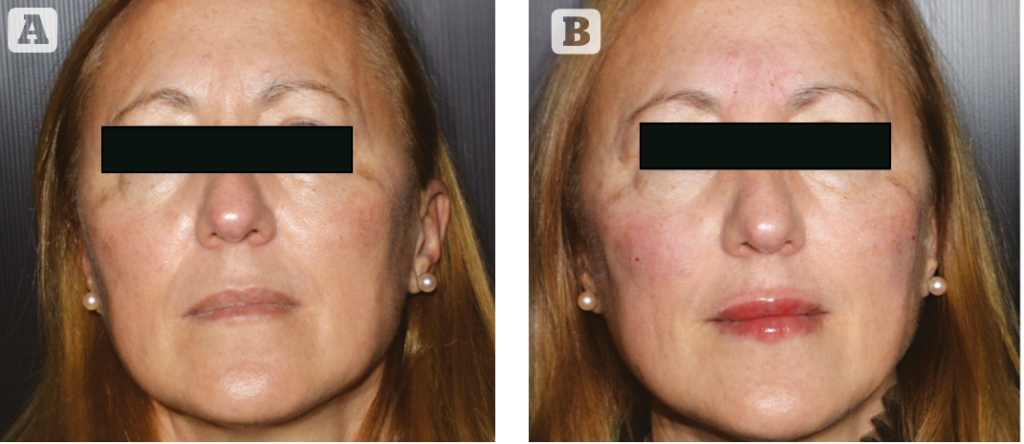
Results
Demographic and baseline characteristics
A total of 39 patients were included in the study, comprising 38 female (97.4%) and 1 male (2.6%), mean age of 57 years (range: 20–78 years.)
Effectiveness
Results from the investigator assessment of GAIS at 1-week post-treatment showed that the majority of patients were ‘very much improved’ (19 patients [48.7%]) or ‘much improved’ (20 patients [51.3%]). No patient was rated as ‘improved’, ‘no change’ and ‘worse’.
The assessment of GAIS 2 weeks post-treatment highlighted that 18 patients were considered ‘very much improved’ (46.15%), 21 patients were rated as ‘much improved’ (53.85%). No patient was rated as ‘improved, ‘no change’, and ‘worse’.
GAIS assessment at 4 weeks post-treatment showed that 17 patients were considered ‘very much improved’ (43.6%), 19 patients were rated as ‘much improved’ (48.7%), 3 patients were rated as ‘improved’ (7.7%). No patient was rated as ‘no change’ or ‘worse’. Investigator GAIS assessment at 24 weeks post-treatment highlighted that 7 patients (17.95 %) were still considered as ‘much improved’, 21 patients (53.85%) were considered ‘improved’, 11 patients (28.2%) were judged as ‘no change’ and no patient was considered ‘worse’ at this time point.
The degree of satisfaction with the cosmetic result was rated for the majority of patients as ‘very satisfied’ (18 subjects) or ‘satisfied’ (20 subjects). Only one patient rated the satisfaction with treatment as ‘indifferent’. No patient was ‘dissatisfied’ or ‘very dissatisfied’.
Safety data
Treatment was well-tolerated, with only temporary adverse events recorded in 17 patients (43.6%). There were no reports of serious adverse events, such as visual disturbance, tissue ischemia, necrosis, or allergy. The reported adverse events were bruising (4 cases), itching (4 cases), redness (6 cases), pain after injection (7 cases), tenderness to touch (12 cases), swelling (4 cases).
Summary
From the analysis of the clinical data, we concluded that the RENÉE range of bionic hyaluronic acid gels have a good effectiveness and safety profile. RENÉE hyaluronic acid gels are easy to inject, and they are highly appreciated by patients and doctors. In conclusion, patients benefit from the aesthetic outcome, facial rejuvenation effect and high safety profile when treated with RENÉE range of products.
Find out more at: https://renee.com.de




