Leah Hardy and William H. George present a novel new chocolate based nutraceutical to complement the post-procedure regeneration process.
Nutricosmetics are foods and supplements designed to improve appearance. They offer consumers a potential complementary therapy in the battle against skin ageing, and practitioners a way to both improve results from treatments and to maximise profits.
This article discusses the growth in the market for nutricosmetics for aesthetic indications, is
The term ‘nutraceutical’ was coined in the late 1980s and is now widely used to describe food products, such as supplements and functional foods, which have a medical benefit. Last year, a report from global accountancy firm KPMG reported that the global market for nutraceuticals was expected to grow to $250 billion by 2018, five times larger than it was in 19991.
A recently evolved sector within the nutraceutical market is for nutricosmetics. These are products specifically formulated with nutrients to enhance and rejuvenate appearance, primarily of the skin, hair, and nails.
These products often claim a plethora of benefits for the skin, such as reducing lines and wrinkles and improving elasticity, clarity, roughness, and pore size as well as boosting collagen production.
A report published in 2015 by market research specialists Global Industry Analysts Inc. estimated that the global market for nutricosmetics is projected to reach $7.4 billion by 20202. This growth is driven by increasing demand from a new breed of consumers who are ageing — one woman in four globally is now over 503 — and keenly aware of the role of nutrition in health. These consumers are increasingly seeking out natural products able to deliver ‘beauty from within’.
These days nutricosmetics are primarily offered in the form of pills, powders that may be added to foods or drinks, specialist foods and ready to drink beauty beverages which can be used alone, as part of a cosmeceutical range or in conjunction with aesthetic procedures.
Nutricosmetics and skin ageing
Skin ageing is driven by intrinsic and extrinsic factors. The latter include hormone imbalances, inflammation, smoking, exposure to UV radiation, and air pollution. These stressors contribute to skin ageing by triggering production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) which harm cell membranes, proteins, and DNA4, 5.
As skin ages, inside the dermis, microcirculation is impaired6 the creation of new vessels is disturbed and flexible fibres are destroyed7.

Many nutricosmetics contain ingredients designed to combat this oxidative stress. For example, oral supplements have recently been launched that claim to both reverse photo-damage and even to provide a certain additional level of SPF within the skin. Studies have shown that oral antioxidants may modify the effect of UV light on human skin8. Recent research has also linked even low level traffic-related air pollution to an increase in oxidative stress leading to a 25% increase in facial lentigines and accelerated skin ageing. Studies suggest that dietary supplementation may play a modulating role in these effects9.
Other studies have even shown that oral supplements may even be effective in treating difficult to resolve skin problems such as melasma10.
Popular ingredients in nutricosmetics include vitamins, peptides, marine proteins and naturally-derived antioxidant compounds such as flavanols, carotenoids, polyphenols, and pre- and probiotics.
Antioxidants, which help counter the effects of oxidative stress by supporting endogenous antioxidant enzymes within skin, are thus key ingredients in nutricosmetic supplements.
Problems within the sector
While many nutricosmetics have been launched over the past decade or more, many have not had the hoped-for success. Reasons for this include products being unpalatable, unpleasant or inconvenient to take. Multiple dose pills that need to be taken with water, or powders that require mixing may be off-putting to busy consumers, particularly given the need for daily consumption.
Some products contain small quantities of active ingredients, or use ineffective actives, or do not have scientific research data to support their claims, leading to consumer scepticism. Factors such as these have lead to poor results, consumer disappointment and the discontinuation of use.
Some nutricosmetics claim results that become apparent only after over many weeks or even months of consumption. In these cases impatient purchasers may opt instead to rely solely on topical formulations that offer instant effects. In addition, sophisticated consumers interested in nutrition may look for natural food products rather than synthetic pills.
To overcome these issues, a novel new nutricosmetic product, Esthechoc, has been created by Dr Ivan Petyaev, an innovator in the pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and functional food industries and developed together with Cambridge Chocolate Technologies Ltd, a UK-based company specialising in the development of high-tech functional chocolate.
What is Esthechoc?
Esthechoc is a highly bioavailable functional food aimed at protecting the skin against premature ageing caused by external elements such as sun damage and air pollution. It offers a combination of powerful antioxidants combined with polyphenol-rich chocolate in a techno-logically innovative yet deliciously indulgent formula. It is designed to encourage daily consumption to maximise results, and is uniquely appealing to consumers. It also has a strong, scientifically proven impact on the metabolism of ageing skin.
It is known that natural cocoa polyphenolic epicatechins in dark chocolate significantly improve skin biomarkers. These biomarkers include an increase in oxygen transport in plasma12, improved skin microcirculation and improved condition of capillaries for skin detoxification and nutrition12, all of which naturally decline with age or when under environmental assault13. Epicatechins also have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties14-15.
The chocolate in Esthechoc is combined with naturally-sourced astaxanthin, one of the most powerful antioxidants known to science.
A daily 7.5g individual portion of Esthechoc provides just 38 kcal and 2 g of sugar. By contrast, to get the same effect from normal dark chocolate, consumers would have to ingest in the region of 100g per day, which would add up to 400 calories to their diet raising the risk of obesity, with its attendant health risks.
The power of astaxanthin
Astaxanthin is a fat-soluble nutrient most prevalent in microalgae. It is a xanthophyll, which is a family of non-provitamin A carotenoids; pigments responsible for the yellow, orange and red colours of many fruits and vegetables. Astaxanthin is the source of the distinctive pink hue of shellfish such as shrimps and crabs, and of salmon and flamingos, which derive their rosy colouring from the astaxanthin in their diet16.
It has been shown to prevent UVA-induced alterations in cellular superoxide dismutase activity and decrease in cellular gluthathione20. It has also been shown to have a pronounced photo-protective effect on human dermal fibroblasts21. Park et al.,22 reported astaxanthin reduced DNA oxidative damage biomarker inflammation.
Astaxanthin can prevent skin thickening and reduce collagen reduction against UV induced skin damage23–24.
Astaxanthin’s unique molecular structure enables it to stay both in and outside the cell membrane. It gives better protection than β-carotene and Vitamin C as it can be positioned either inside the lipid bilayer (β-carotene) or in the cytosol (outside the cell membrane — vitamin C)25–26.
Astaxanthin is a potential therapeutic agent against atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease27 and in studies has showed significant anti-tumor activity28.
Polyphenols
Polyphenolic compounds are plant nutraceuticals showing a huge structural diversity, including chlorogenic acids, hydrolyzable tannins, and flavonoids (flavonols, flavanones, flavan-3-ols, anthocyanidins, isoflavones, and flavones). Most of them occur as glycosylated derivatives in plants and foods. In order to become bioactive in the human body, these polyphenols must undergo diverse intestinal transformations, due to the action of digestive enzymes, but also by the action of microbiota metabolism. After elimination of sugar tailoring (generating the corresponding aglycones) and diverse hydroxyl moieties, as well as further backbone reorganizations, the final absorbed compounds enter the portal vein circulation towards the liver (where other enzymatic transformations take place) and from there to other organs, including behind the digestive tract or via blood towards urine excretion. During this transit along diverse tissues and organs, they are able to carry out strong antiviral, antibacterial, and antiparasitic activities29.
What is unique about Esthechoc?
Chocolate owes its texture to the tempering process, which involves heating and cooling chocolate to create specific crystals within the product. During the proprietary manufacturing systems behind Esthechoc, unique micellar technology naturally co-crystalises epicatechins and astaxanthin, creating astacelles. In the body, these create a super-additive effect, making the actives more bioavailable and ten times more powerful than when ingested alone.
Astacelles deliver the actives lymphatically rather than portally, and this avoids first-pass metabolism by the liver and increases bioavailability30.
Astacelles also protect the actives from in the GI tract from oxidation, stomach acidity, and gut flora, ensuring they are delivered to the point of absorption in the intestine in their unmodified forms, enabling greater bioavailability. The manufacturing process also decreases levels of caffeine and theobromine in chocolate as these compounds may have a negative action on the cardiovascular system in high doses31,32. This ensures Esthechoc shows measurable efficacy even when taken in small quantities.
To test the efficacy of Esthechoc, volunteers aged 45 –70 years old were recruited for a four week, double-blind study comparing Esthechoc to a control of dark chocolate plus 5 mg astaxanthin capsules33.

Researchers discovered Esthechoc’s astacelle technology resulted in the actives becoming 59% more bioavailable than when taken as dark chocolate consumed with astaxanthin capsules. The antioxidant activity of Esthechoc with 4 mg of astaxanthin was greater than even 10 mg of the carotenoid in capsule form33.
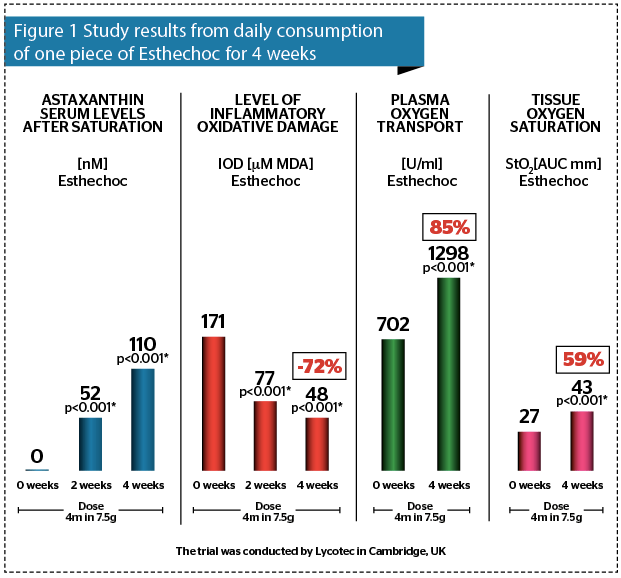
Clinical studies conducted at Addenbrooke’s Hospital in Cambridge found that after four weeks of consuming a single daily piece of Esthechoc, oxygen saturation of tissues increased by 59% and oxygen transport in plasma improved by 85%. Inflammatory oxidative damage was reduced by 72% (Figure 1). The research proved that both biochemical and metabolic conditions of blood and skin were improved. Better skin nourishment was noticed thanks to microcirculation improvement and higher saturation with oxygen. Skin detoxification processes and protection against free radicals were also intensified33.
This data demonstrates that Esthechoc can not only effectively inhibit oxidative and inflammatory markers but also improve age-associated depression of the respiratory parameters of the peripheral tissues, including skin.
Patient safety
Practitioners are increasingly looking to maximise both profits and the results of the surgical and non-surgical treatments they offer in clinics by offering patients complementary skincare and nutricosmetics. It is therefore important that any nutricosmetics offered are both safe and non-contraindicated with aesthetic procedures.
Because Esthechoc trials show positive effects on skin health and adhesive tissues, such as a reduction in free radicals and increased oxygenation, the product can optimise recovery from any intervention in aesthetic medicine, dermatology, aesthetic dermatology and plastic surgery.
Esthechoc is an effective nutraceutical that can be successfully used as a working food supplement peri-operatively and prior and/or post any procedure where optimal regeneration and wound healing is required.
Safety is a vital consideration when recommending a nutraceutical. While some vitamins present a risk of side effects with overdose, no toxic effects from astaxanthin have been observed even at high doses34,35. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved the use of astaxanthin as a food ingredient for human consumption since as far back as 199936.
Esthechoc components are resistant to stomach acid and they are not metabolized in the liver. They go directly through the lymph system and the thoracic duct to the venous angle and from there directly to the tissues. Because of the way Esthechoc is metabolised it does not cause elevated blood sugar levels, making it safe for diabetics.
Indeed astaxanthin could reduce the oxidative stress caused by hyperglycemia in pancreatic β-cells and also improve glucose and serum insulin levels37. It was also shown to improve insulin sensitivity in both spontaneously hypertensive corpulent rats and mice on high fat plus high fructose diets was observed after feeding with astaxanthin38 Another study demonstrated that astaxanthin prevents diabetic nephropathy by reduction of the oxidative stress and renal cell damage39.
Esthechoc is a food and is therefore safe for most people, including diabetics, vegans and those with gluten intolerance. Only pregnant women, children and those sensitive to caffeine should take advice from their doctor before eating. It is complementary to all skin care products.
Consumers are more likely to feel confident and motivated to purchase a nutricosmetic or nutraceutical if they understand how it works and trust their practitioner’s recommendation.
Awards help consumers feel confident that their chosen product is reliable and effective. In 2015 Esthechoc won the Beauty Challenger Award Grand Prix and the Beauty Challenger Award for Skincare at the prestigious major trade fair Beyond Beauty in Paris. It was also nominated for Product Innovation of the year at the 2016 Aesthetics Awards.
Conclusion
The use of dietary supplements for the rejuvenation of ageing skin has gathered a significant body of positive scientific evidence and is a rapidly growing market. This unique chocolate-based nutraceutical offers consumers an enjoyable, clinically proven adjunct to treatment with other cosmetic modalities. It can help consumers boost or maintain results at home in an easy, risk-free manner. This provides a valuable addition to the practitioner’s offer to patients with the potential to increase consumer satisfaction, build loyalty and increase profits.
For more information, visit: www.cambridgechocolate.com





